苯酚酶消化高苯酚,它不含消化蛋白质的酶,所以对患有溃疡的人比较能够容忍。
Description
![]()
![]()
Phenol Assist™ is an enzyme designed to help digest part of the cell wall
structure of plant cells in fruits, vegetables and grains. Doing so opens
the cell and allows the process of phenol digestion to occur.
When an apple or a pear is sliced open and is left out for a while, the tissue
of the fruit turns brown. That browning process is the result of the
natural enzyme present in fruits, "phenolase," oxidizing the fruit
tissue. This process cannot occur until the cell wall is broken and
oxygen gets into the cells. Phenol Assist™ gets this process going and
therefore supports sulfation by reducing the phenolic load on the body's
sulfation capacity.
Phenols are compounds with a specific
chemical structure of an aromatic ring plus a hydroxyl group. They are
found in fruits, vegetables, some grains and nuts, flavorings and spices.
A salicylate is a type of phenolic compound. Phenols and polyphenols have
antioxidant qualities and protective functions, which make some of them
beneficial and desirable for most individuals.
An important chemical process that occurs in body tissues is called sulfation.
Sulfation is the movement of sulfate (sulfur plus oxygen) ions from one body
tissue to another. Sulfating molecules change the molecules’ character
and behavior and how they act in the body. Connective tissue is sulfated
for structural reasons and neuron tissue is sulfated to provide a protective
sheath. Sulfation also causes molecules to vary in activity, solubility,
and mobility. For the body to work properly, these sulfation processes
must occur.
What is the relationship between phenolic compounds and sulfation? Phenols and salicylates use up a lot of sulfate in the body in order to be broken down. In other words, the phenols and salicylates compete for the body's sulfate stores. In certain individuals, breaking down phenolic compounds can provide a benefit by supporting the sulfation mechanism.
Phenol Assist™ contains a variety of enzymes to accomplish cell wall digestion, and other enzymes to assist in the total digestion of fruits, vegetables, grains, and spices. Below is a brief description of the enzymes present:
• Xylanase
makes grains, fruits and vegetables that utilize xylose in their structure more
digestible by breaking
some of the xylan bonds.
• CeraCalase™ is a proprietary blend of the National Enzyme Company that aids the breakdown of plant and
fruit structures.
• Cellulase
helps digest the cellulose fibers surrounding plant cells.
• Beta-Glucanase is an enzyme that breaks down
glucan structures in fruits and grains.
• Phytase breaks organic-phosphate bonds, which helps destroy phytins and phytic acid, thereby ensuring that
important minerals are not complexed and transported unused out of the body.
• Alpha
Amylase is an enzyme that helps digest starches and complex sugars present in
plants.
• Glucoamylase aids digestion of polysaccharides
and polymeric chains of glucose.
• Alpha-Galactosidase hydrolyzes bonds that hold galactose, thereby
freeing the glactose
for its enzyme stimulating function
involving DPP-IV.
Suggested Use: One capsule with meals consisting of phenol containing
foods. Start with ¼ to ½ capsule and gradually increase this dose to the
amount that provides optimal digestion of foods.
The dose can be adjusted according to the specific needs of the
individual. With small meals or snacks, smaller doses may be sufficient
to provide adequate digestion of these foods. Avoid mixing with food or
beverages that will be heated above 130° F as the activity of the enzymes will
be adversely affected.
Enzymes should be taken at the beginning or early on in the meal to ensure
appropriate digestion. The capsules may be swallowed whole or opened and
mixed with food or beverages.
We recommend that Phenol Assist™ be used with Kirkman's
Phenol Assist™ Companion (0262-090) to help sulfation.
A list that details phenolic and salicylate content of foods follows:
VERY HIGH
Apricots
Berries and cherries
Oranges and tangerines
Pineapple
Red grapes
Tomatoes
Peppers
Mint
Anise (licorice)
Olives
Dill
HIGH TO MODERATE
Apples
Grapefruit
Peaches and mangos
Watermelon
Broccoli and spinach
Carrots
Lettuce and chinese vegetables (except iceberg/low)
Most nuts and seeds
Onions
LOW TO NEGLIGIBLE
Bananas
Pears
Cabbage
Celery
Potatoes
Fats and oils
Sugars
Soy milk
Free Of
Sugar, soy, wheat, casein, gluten, artificial flavorings or colorings.
Warnings:
DO NOT ALLOW THE POWDER IN THE CAPSULES TO GET INTO THE EYE OR CONTACT THE SKIN. KEEP OUT OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN. STORE IN A COOL DRY PLACE AND TIGHTLY CAPPED. CERECALASE IS A REGISTERED TRADEMARK FOR A PROPRIETARY BLEND OF NATIONAL ENZYME COMPANY 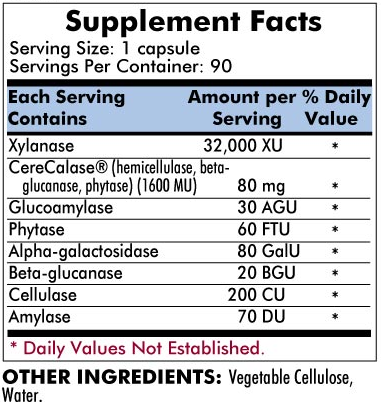
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food & Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease.